Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation: A Semi-supervised Approach
Published in Iberian Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, 2019
Recommended citation: Ghosh T.K., Saha S., Rahaman G.M.A., Sayed M.A., Kanagasingam Y. (2019) Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation: A Semi-supervised Approach. In: Morales A., Fierrez J., Sánchez J., Ribeiro B. (eds) Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis. IbPRIA 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11868. Springer, Cham https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-31321-0_9
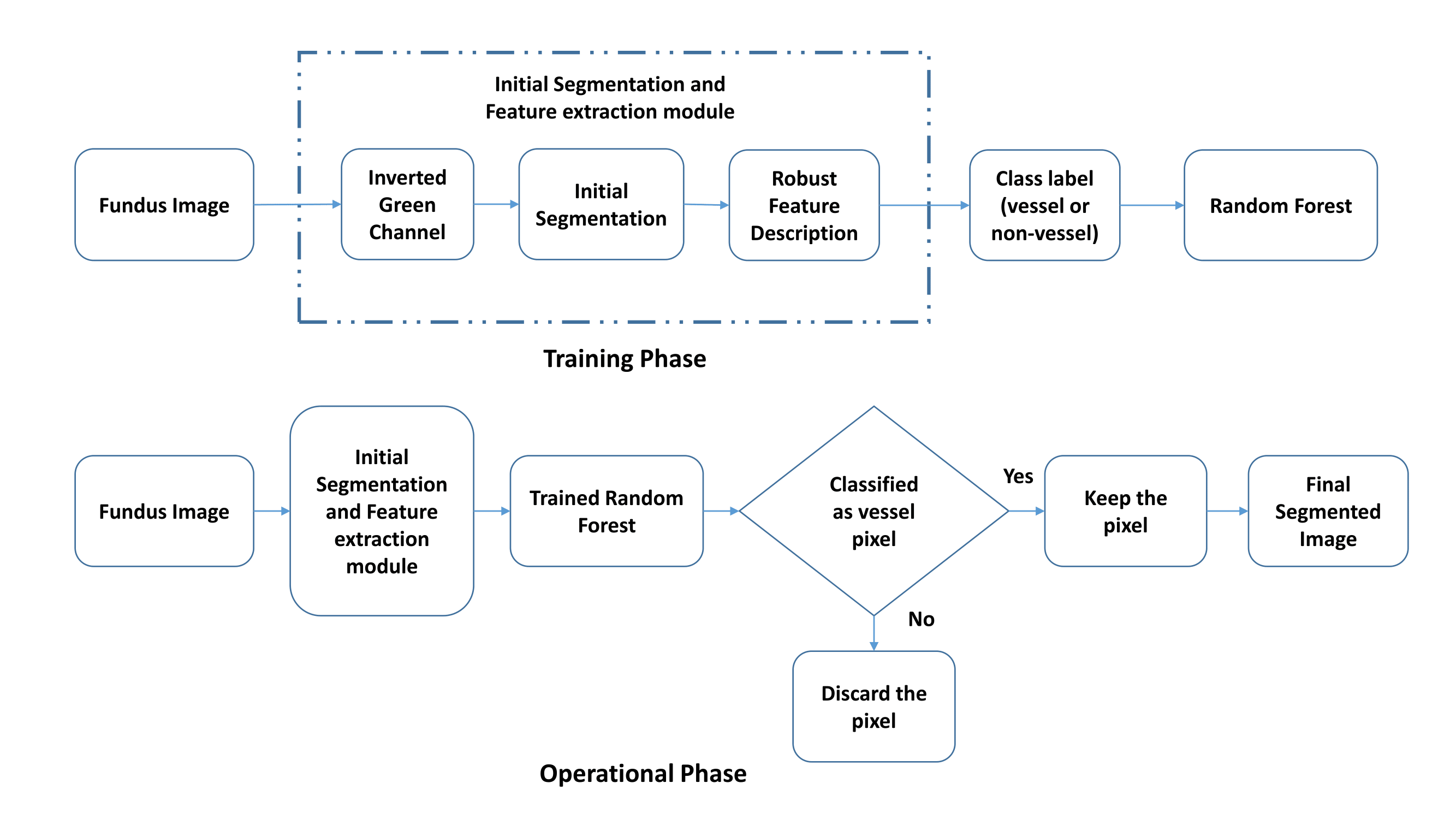 Segmentation of retinal blood vessels is an important step in several retinal image analysis tasks. State-of-the-art papers are still incapable to segment retinal vessels correctly, especially, in presence of pathology. In this paper an innovative descriptor named Robust Feature Descriptor (RFD) is proposed to describe vessel pixels more uniquely in the presence of pathology. For accurate segmentation of blood vessels, the method combines both supervised and unsupervised approaches. Extensive experiments have been conducted on three publicly available datasets namely DRIVE, STARE and CHASE_DB1; and the method has been compared with other state-of-the-art methods. The proposed method achieves an overall segmentation accuracy of 0.961, 0.960 and 0.955 respectively on DRIVE, STARE and CHASE_DB1 datasets, which are better than the state-of-the-art methods in comparison. The sensitivity, specificity and area under curve (AUC) of the method are respectively 0.737, 0.981, 0.859 on DRIVE dataset; 0.805, 0.972, 0.889 on STARE dataset; and 0.763, 0.969, 0.866 on CHASE_DB1 dataset.
Segmentation of retinal blood vessels is an important step in several retinal image analysis tasks. State-of-the-art papers are still incapable to segment retinal vessels correctly, especially, in presence of pathology. In this paper an innovative descriptor named Robust Feature Descriptor (RFD) is proposed to describe vessel pixels more uniquely in the presence of pathology. For accurate segmentation of blood vessels, the method combines both supervised and unsupervised approaches. Extensive experiments have been conducted on three publicly available datasets namely DRIVE, STARE and CHASE_DB1; and the method has been compared with other state-of-the-art methods. The proposed method achieves an overall segmentation accuracy of 0.961, 0.960 and 0.955 respectively on DRIVE, STARE and CHASE_DB1 datasets, which are better than the state-of-the-art methods in comparison. The sensitivity, specificity and area under curve (AUC) of the method are respectively 0.737, 0.981, 0.859 on DRIVE dataset; 0.805, 0.972, 0.889 on STARE dataset; and 0.763, 0.969, 0.866 on CHASE_DB1 dataset.
